Validation Block
About Validation
Validations are a type of logic blocks that are designed for assessing specific conditions and yielding a clear outcome: "true" when the condition is met, or "false" when it isn't. This direct approach ensures accurate data validation and efficient decision-making.
For instance, whether you're confirming the presence of a value within a list, validating whether a certain value is null, or even enabling the setup of conditional scenarios – validations have you covered. You'll receive a clear outcome that guides your next steps in the project.
Supported Data types
The validation block evaluates data and returns a clear outcome, either true or false. Its return type is always boolean, but it's equipped to validate a variety of data types using different built-in functions and to facilitate these validations, the block utilizes built-in functions that fall under:
Let's now examine the main data types that the validation block can evaluate and validate:
| Data Type | Description | Supported Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Integer, Float, Decimal, Money | Assesses numeric values against set conditions. | Is Equal To, Is Greater Than, Is Greater Than Or Equal To, Is Less Than, Is Less Than Or Equal To, Is Not Equal To, Null, Not Null |
| Date/Time | Checks date and time entries for accuracy and relevance. | If Condition, Null, Not Null |
| String | Evaluates textual data against established patterns or criteria. | Contains SubString, Does Not Contain Substring, Does Not End With - Does Not Start With, Ends With,Starts With, Not Null Or Empty String, Null Or Empty String, Null, Not Null |
| Boolean | Assesses true/false conditions. | Is True, Is False, Null, Not Null, AND, OR, If Condition |
Now that we've seen the data types and functions, let's look at some real examples to see how they work together.
Practical Examples
Here are some examples demonstrating how the validation block can be utilized. For detailed examples about each function within the validation block, refer to the tutorials section.
Example 1:
A validation block that prevents users from submitting an empty email using the Not Null Or Empty String function.
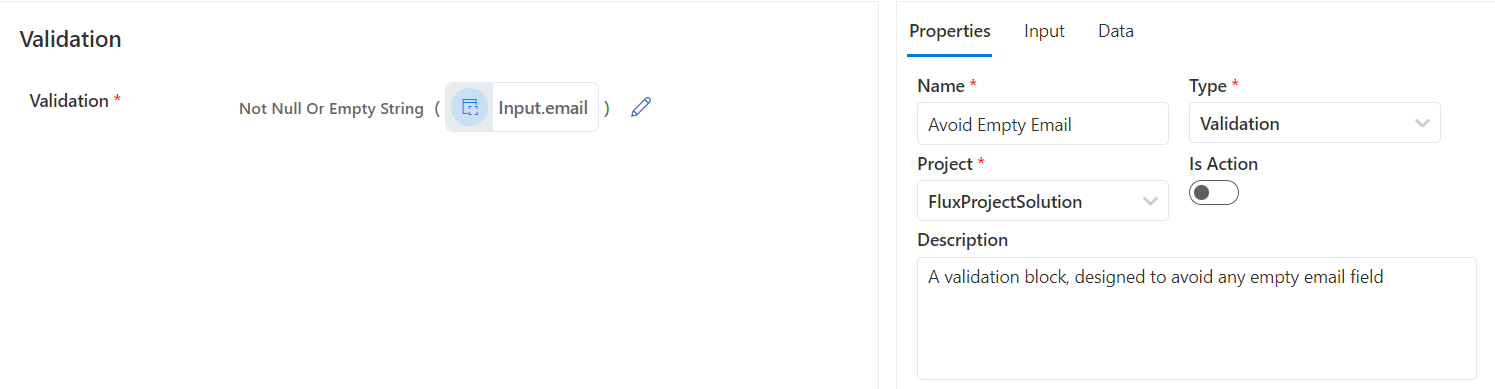 Figure 1: Validation Block To Avoid Empty fields
Figure 1: Validation Block To Avoid Empty fields
Example 2:
A validation Block designed to verify if the country entered by the user is valid by cross-referencing it with a list of recognized countries using the contains item function.
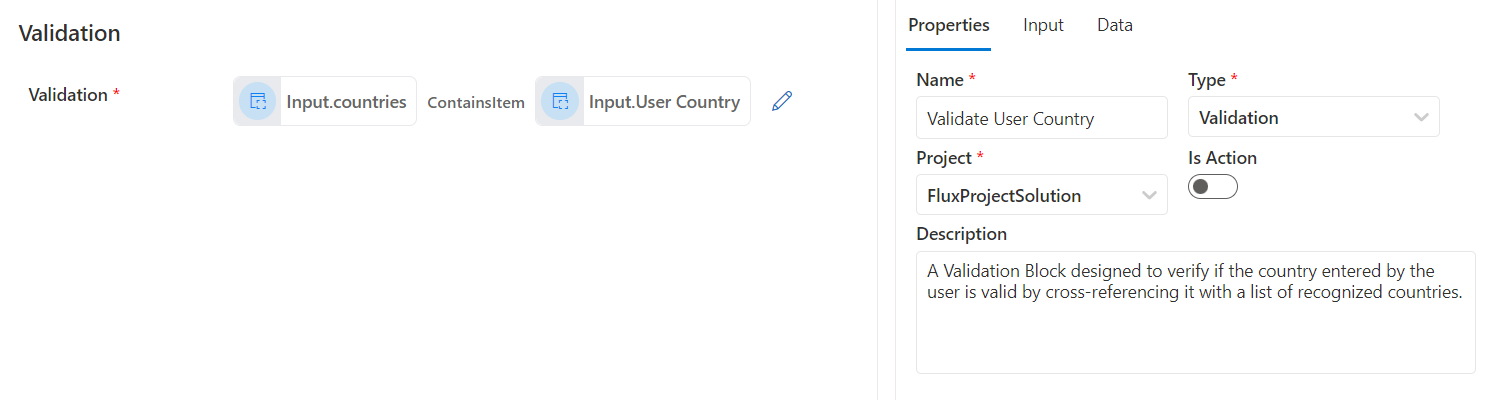 Figure 2: Validation Block To Check Country Existences
Figure 2: Validation Block To Check Country Existences
Example 3:
A validation Block to determine whether a user's age aligns with the defined age brackets. If the age is within bounds, the user can continue; if not, they're restricted. This assessment leverages the If Condition, AND operator, Is Greater Than, Is Less Than Or Equal To functions.
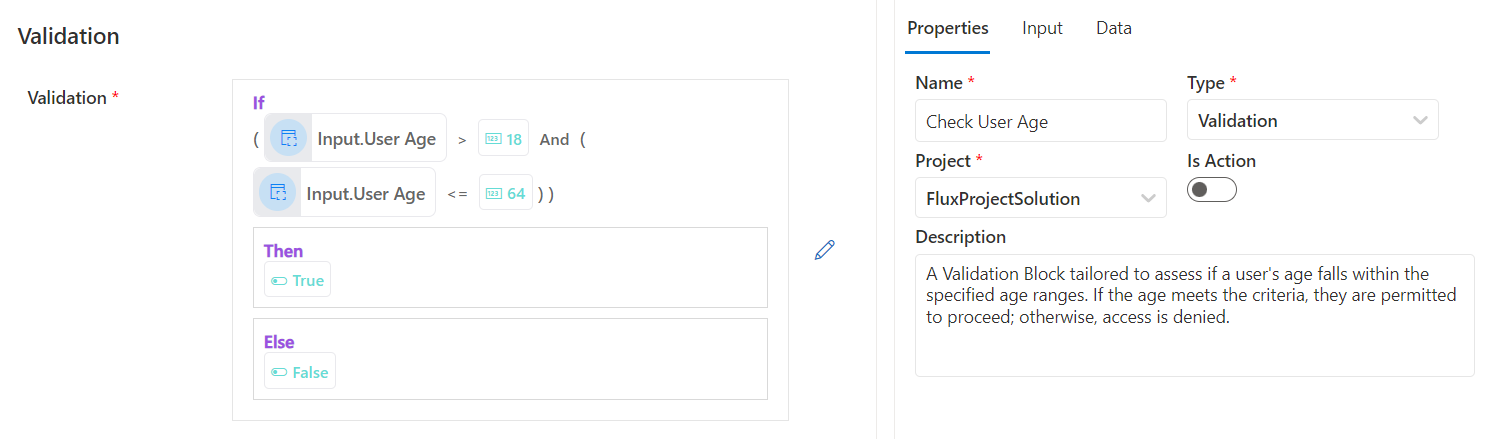 Figure 3: Validation Block To Validate User Age
Figure 3: Validation Block To Validate User Age
What's Next? Now that we've looked at validation blocks, it's time to shift our focus to another essential component: the Validation Set. In the next section, we'll see how validation sets help us keep our data accurate and in the right format.