Decision Tree Block
About Decision Tree
Decision trees a type of logic blocks that offers a visual representation of decision-making pathways. They help you navigate through a series of decisions based on a set of conditions where each branch represents a potential outcome, making it easier to understand and analyze the different possibilities.
Benefits of Decision Tree
- Guided Decision-Making: Decision trees provide a clear, visual flowchart for consultants to follow when assessing complex scenarios or making decisions. This step-by-step approach ensures consistency in decision-making processes, especially when multiple criteria need to be considered.
- Streamlining Complex Processes: In CRM systems, multiple factors can influence a single decision, such as customer data, purchase history, or interaction logs. Decision trees simplify this by breaking down complex decision-making processes into manageable steps, enabling consultants to easily navigate through diverse scenarios and reach an outcome efficiently.
- Easy to Understand and Communicate: Decision trees visually represent decision logic, making it easier for consultants to explain the reasoning behind certain processes or decisions to stakeholders, even if they aren't technically inclined.
Decision Tree Components
Conceptual Components:
These are the basic building blocks of the decision tree, helping us understand what we're evaluating and what results we want:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Inputs | The information we start with. This could be details about a customer, product, or any other data point we need to make decisions on. Where the available data types are (integer, decimal, money, float, boolean, string, date/time) |
| Decisions | The questions we ask about our inputs. For instance, "Has the customer made a purchase in the last year?" |
| Outcomes | The final results or actions we get after looking at our inputs and asking our questions. This could be something like "Send a thank you email." |
Structural Elements:
These parts help us visually understand how the decision-making process flows from start to finish:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Root Node | This is our starting point, often the main question or data point we're focusing on. |
| Decision Nodes | These are the points where we ask questions about our data. Depending on the answer, we move to the next appropriate step in the tree. |
| Terminal Nodes | These are our end points, where we've asked all our questions and arrive at a final decision that derive the outcome |
| Branches | The lines that connect the steps in our tree. They show us which direction to go after each decision or question. |
How Decision Trees Work
Decision trees provide a visual and structured way to make decisions based on certain criteria. They break down a decision-making process into a series of nodes, each representing a condition or outcome. Now, Let's look at a practical example of how a decision tree can be used. We'll assess if a student is ready to graduate with a bachelor's degree based on their academic progress.
Scenario: A Student's Bachelor's Degree Eligibility
1. Root Node:
- Question: How many semesters has the student completed? This is the starting point of our decision-making process. Depending on the number of semesters completed, we branch out into two pathways.
2. Decision Node 1 (After Root Node):
- Question: Has the student completed 8 semesters (typical duration for a bachelor's degree)?
- Yes Branch: Move to the next decision node about the total grades achieved.
- No Branch: Directly leads to a leaf node indicating the student is "Not Eligible for Bachelor's Degree".
3. Decision Node 2 (After Yes Branch of Decision Node 1):
- Question: Are the student's total grades above the passing threshold (e.g., 65%)?
- Yes Branch: Leads to a leaf node with the outcome.
- No Branch: Directly leads to a leaf node indicating the student is "Not Eligible for Bachelor's Degree".
4. Terminal Nodes:
- If both conditions of completing 8 semesters and achieving grades above the passing threshold are met, the terminal node is reached with the outcome "Eligible for Bachelor's Degree".
- If any of the conditions are not met, another leaf node is reached with the outcome "Not Eligible for Bachelor's Degree".
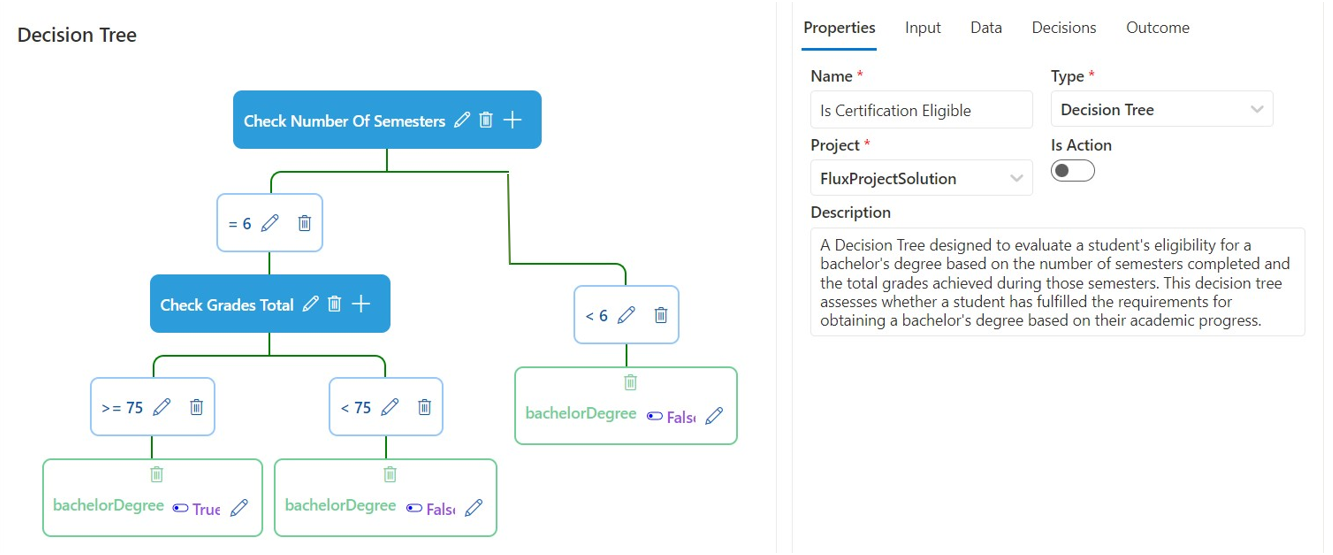 Figure 5: Decision Tree Block Example
Figure 5: Decision Tree Block Example