Logic Block As a Function
About
FlowOn Logic Blocks are advanced tools within the FlowOn system designed to empower users to create custom functions for specialized functionalities not covered by built-in functions. These versatile blocks are adept at working with a wide range of data types including strings, integers, money, entities, and date/time. They are engineered to accept optional inputs and reliably produce the desired outputs. A key characteristic of these blocks is their side-effect-free nature, ensuring they solely focus on delivering an end result based on the executed logic.
A significant advancement in the FlowOn system is the integration of Logic Blocks as expressions. This enhancement allows for seamless execution of these blocks in various contexts – be it within other blocks, flows, and across different workflow stages, or as part of a business process stage. Particularly in transition guards of business processes, they play a crucial role in computing values that dictate the flow's progression.

The FlowOn Expression Builder further refines this functionality. It enables users to effortlessly utilize any pre-created Logic Block, tailoring it to the specific return value required. This feature is particularly beneficial in scenarios where decision-making hinges on specific data types. For instance, in a business process transition guard that requires a boolean value for decision-making, the Expression Builder intelligently filters and presents only those Logic Blocks that output boolean types. This targeted approach not only streamlines the process but also ensures precision and relevance in the functions executed, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the business process management.
Logic Block Parameters
| Parameter | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | No | Various (Boolean, String, Integer, Decimal, Entity, Money, Date/Time, Float, etc.) | A list of inputs that the logic block can process. These inputs are not mandatory but can be used to feed data into the logic block for processing. The types of inputs the block can handle include basic data types like Boolean, String, Integer, and Decimal, as well as more complex types like Entity, Money, Date/Time, and Float. |
| Output | Varies based on the logic block's return type | The output produced by the logic block upon execution. |
Example
In this example, we demonstrate the execution of a 'validation set' logic block within the FlowOn BPM system. The primary function of this logic block is to validate employee travel details as part of the reimbursement process. After processing the inputs, it returns a boolean value (true or false), which is determined based on specific validation rules set within the logic block.
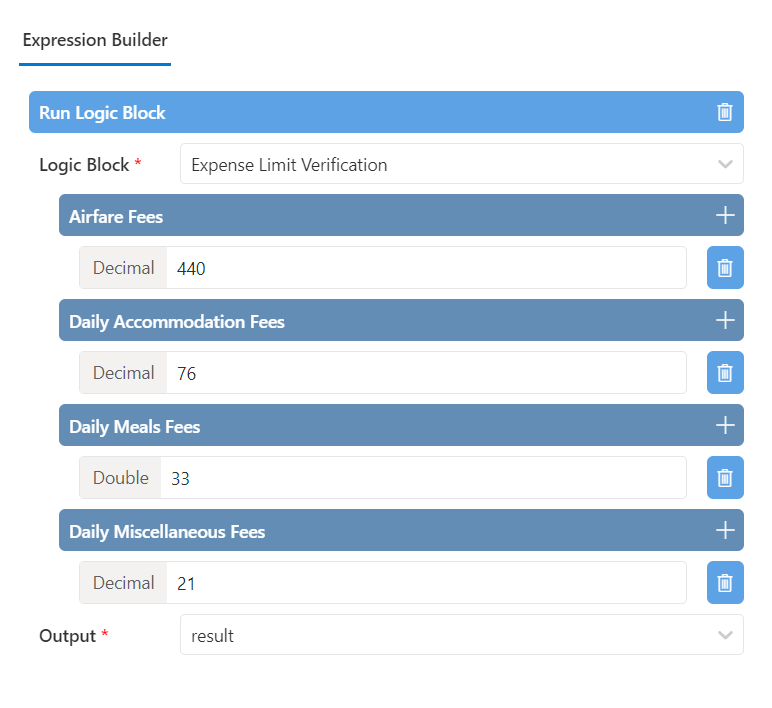
In the illustrated example, a pre-defined logic block titled 'Validate Travel Details' is employed. The process involves:
Passing Inputs: Essential information pertaining to the employee's travel, such as dates, destinations, expenses, etc., are inputted into the logic block. This data is critical for conducting a thorough validation.
Executing Validation Logic: The logic block processes these inputs according to its embedded validation rules. These rules might include checks for policy compliance, budget limits, and correctness of the details provided.
Returning the Result: Based on the evaluation, the logic block outputs a boolean result. This output is either true, indicating that the travel details adhere to all validation criteria, or false, signaling a discrepancy or non-compliance.
Process Advancement: The boolean result then informs the subsequent steps of the reimbursement process. For instance, a true result may lead to the process advancing to the reimbursement stage, while a false result could trigger additional review or correction steps.